Reference
Refer to this page for details about how Cloudflare orchestrates VPN connectivity to your cloud networks.
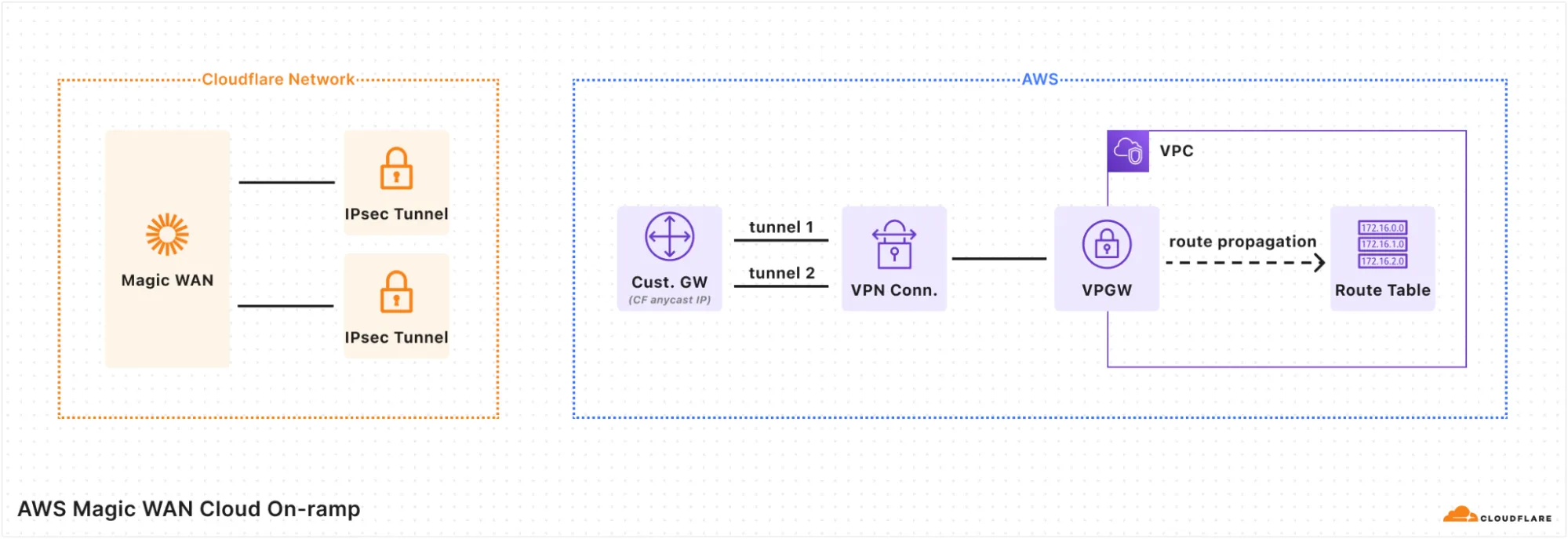
When using Magic Cloud Networking to automatically create on-ramps to your AWS account, you should be aware of the following configuration changes Cloudflare will make on your behalf:
- Cloudflare will create a new customer-managed prefix list named Magic WAN and Cloudflare Edge populated with your Magic WAN Address Space prefixes and the IPv4 address ranges for Cloudflare's global network servers (the latter prefixes are necessary if you use any Cloudflare L7 processing features). You must create rules in your Network Security Groups (NSGs) allowing traffic to/from this prefix list in order to have connectivity with Magic WAN. (The prefix list will contain around 15 to 25 entries, which each count against the rules-per-security-group quota for NSGs in your AWS account.)
- Cloudflare will create a Virtual Private Gateway and attach it to your Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). If an existing Virtual Private Gateway is already attached to the VPC, on-ramp creation will fail.
- Cloudflare will enable route propagation from the Virtual Private Gateway into all route tables in your VPC. This will result in a route for each prefix in your Magic WAN Address Space targeting the gateway.
- Cloudflare will add a route in Magic WAN for each IPv4 CIDR block in your VPC.
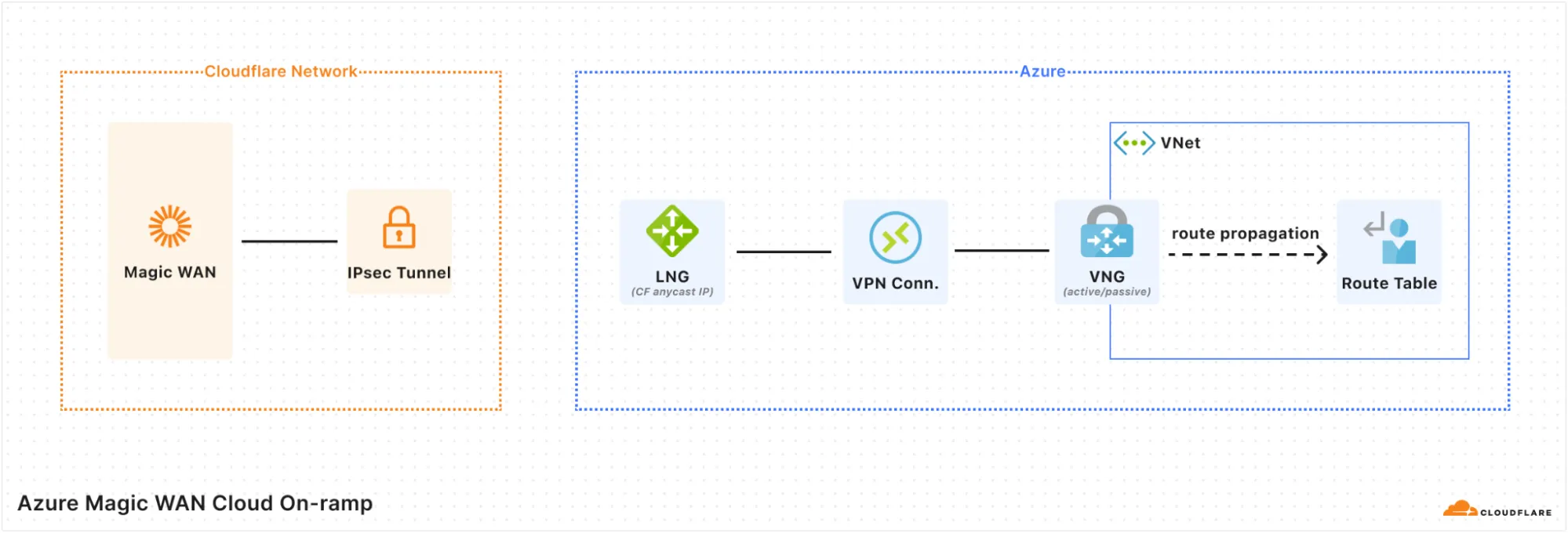
When using Magic Cloud Networking to automatically create on-ramps to your Azure account, you should be aware of the following configuration changes Cloudflare will make on your behalf:
- Cloudflare will create a Virtual Network Gateway in your Virtual Network (VNet). Virtual Network Gateways in Azure require a subnet named
GatewaySubnet. Cloudflare will create aGatewaySubnetif one does not already exist in your VNet. If there is not enough unused address space left in your VNet to create a/27subnet for theGatewaySubnet, or if aGatewaySubnetexists but does not have enough address space left for a Virtual Network Gateway, on-ramp creation will fail. - Cloudflare will enable gateway route propagation on all route tables in your VNet. This will result in a route for each prefix in your Magic WAN Address Space pointing to the gateway. If your VNet has other Virtual Network Gateways, their routes will also propagate to your route tables. If you delete the on-ramp, route propagation will not be disabled.
- By default, Network Security Groups in Azure contain Allow rules for outbound/inbound traffic to/from the
VirtualNetworkservice tag, which includes Virtual Network Gateway address space (and therefore your Magic WAN Address Space). If you do not want all resources in your VNet to be accessible from Magic WAN, add the appropriate Deny rules to your Network Security Groups (NSGs). - Cloudflare will add a route in Magic WAN for each IPv4 address range in your VNet.
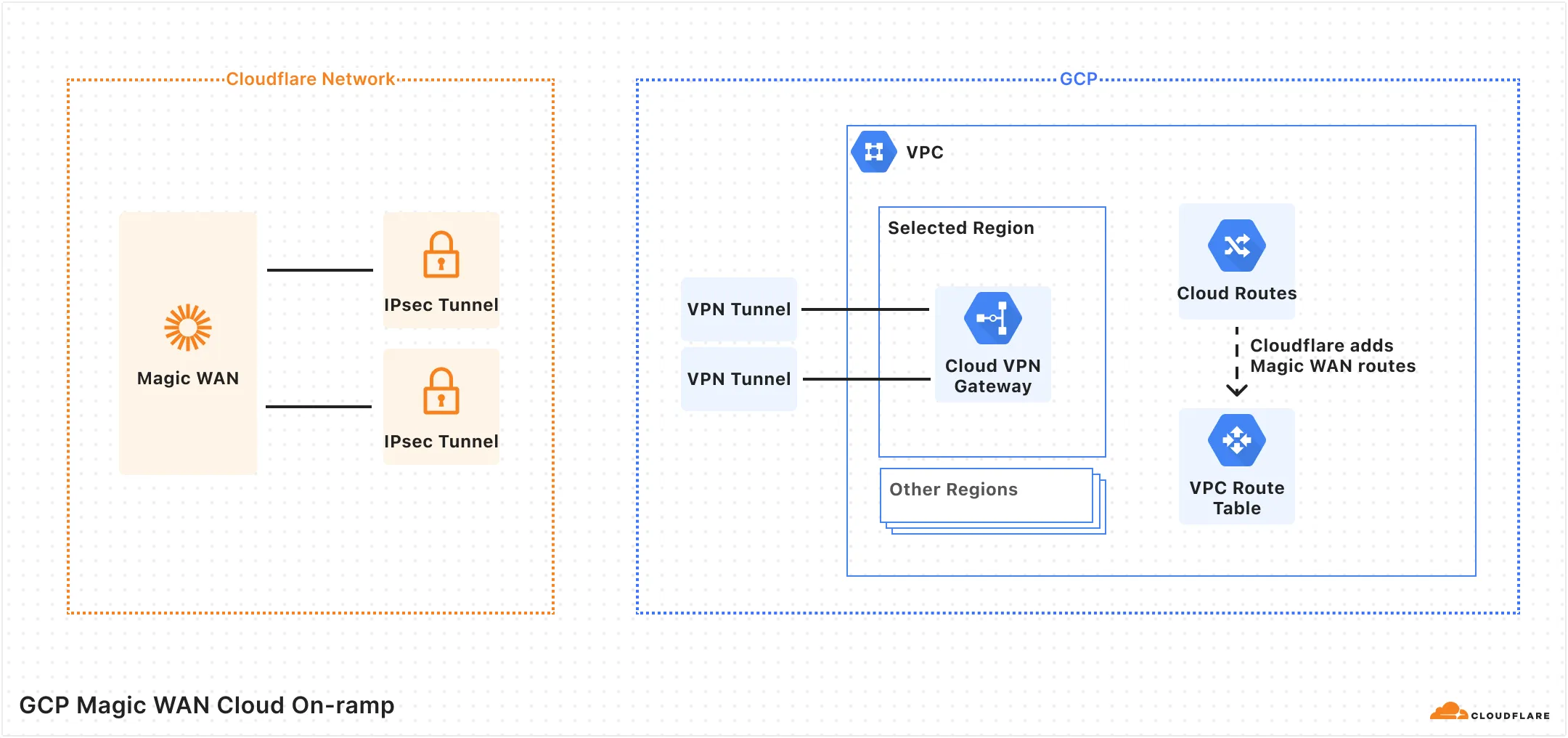
When using Magic Cloud Networking to automatically create on-ramps to your Google Cloud Platform (GCP) account, you should be aware of the following configuration changes Cloudflare will make on your behalf:
- Cloudflare will reserve a public Internet routable IP address from GCP.
- Cloudflare will create a VPN Gateway and two VPN Tunnels in the region you specify.
- Cloudflare will create routes for each prefix in your Magic WAN Address Space within your VPC pointing to the VPN Tunnels.
- Cloudflare will add routes in Magic WAN for all subnet CIDR prefixes in your VPC. This includes all regions within the VPC. Traffic bound for a region other than the VPN Gateway's region will be subject to GCP's Inter-region Pricing ↗.
- Traffic sent to and from your VM instances through the VPN Tunnels is still subject to VPC firewall rules, and may require further configuration ↗.
Magic Cloud Networking discovers the following resource types.
- AWS Customer Gateway
- AWS EC2 Managed Prefix List
- AWS EC2 Transit Gateway
- AWS EC2 Transit Gateway Prefix List
- AWS EC2 Transit Gateway VPC Attachment
- AWS Egress Only Internet Gateway
- AWS Internet Gateway
- AWS Instance
- AWS Network Interface
- AWS Route Table
- AWS Route Table Association
- AWS Security Group
- AWS Subnet
- AWS VPC
- AWS VPC IPv4 CIDR Block Association
- AWS VPC Security Group Egress Rule
- AWS VPC Security Group Ingress Rule
- AWS VPN Connection
- AWS VPN Connection Route
- AWS VPN Gateway
- Azure Application Security Group
- Azure Load Balancer
- Azure Load Balancer Backend Address Pool
- Azure Load Balancer NAT Pool
- Azure Load Balancer NAT Rule
- Azure Load Balancer Rule
- Azure Local Network Gateway
- Azure Network Interface
- Azure Network Interface Application Security Group Association
- Azure Network Interface Backend Address Pool Association
- Azure Network Interface Security Group Association
- Azure Network Security Group
- Azure Public IP
- Azure Route
- Azure Route Table
- Azure Subnet
- Azure Subnet Route Table Association
- Azure Virtual Machine
- Azure Virtual Machine Gateway Connection
- Azure Virtual Network
- Azure Virtual Network Gateway
- Azure Virtual Network Gateway Connection
- Google Compute Address
- Google Compute Forwarding Rule
- Google Compute Global Address
- Google Compute HA VPN Gateway
- Google Compute Interconnect Attachment
- Google Compute Network
- Google Compute Network Firewall Policy
- Google Compute Network Firewall Policy Rule
- Google Compute Route
- Google Compute Router
- Google Compute Subnetwork
- Google Compute VPN Gateway
- Google Compute VPN Tunnel